Making streets safer for women: A women-centric walkability index for Kollam’s urban future, India
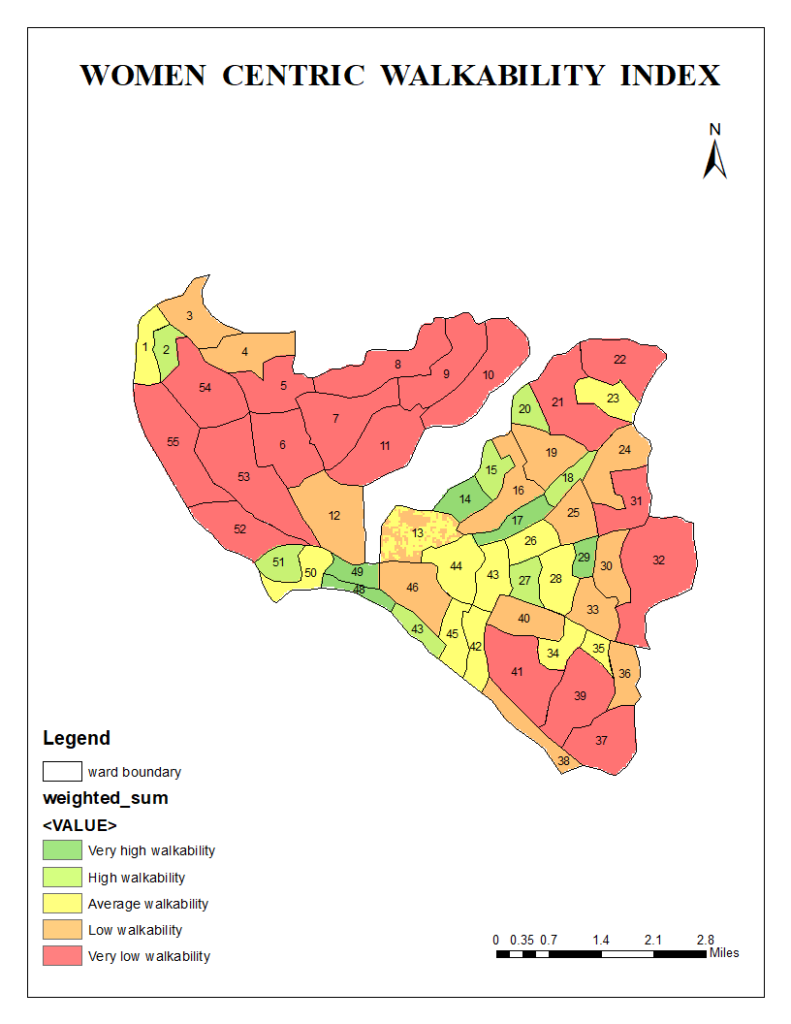
This study introduces the Women-Centric Walkability Index, addressing factors influencing women’s walking experiences in urban areas. Analyzing fifty-five wards in Kollam Corporation, Kerala, we identified key indicators like well-maintained sidewalks, street lighting, safety measures, and access to public amenities that enhance women’s walkability. Using the Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS analysis, our research highlights the need for safer, more accessible, and comfortable walking environments for women, benefiting all pedestrians.
Shared mobility as a mean to tackle transport poverty in deprived neighbourhoods

Shared mobility hubs that offer (electric) bikes and cars can be a sustainable solution that enables people to expand their mobility options while protecting cities’ environment by reducing private car use and encouraging cycling. We interviewed residents of a deprived neighbourhood in Utrecht, the Netherlands, to understand their mobility needs and views on a recently implemented shared mobility hub in their neighbourhood, identifying potential obstacles in the process.
Making cities walkable for caregivers: bridging urban complexity and mobility justice
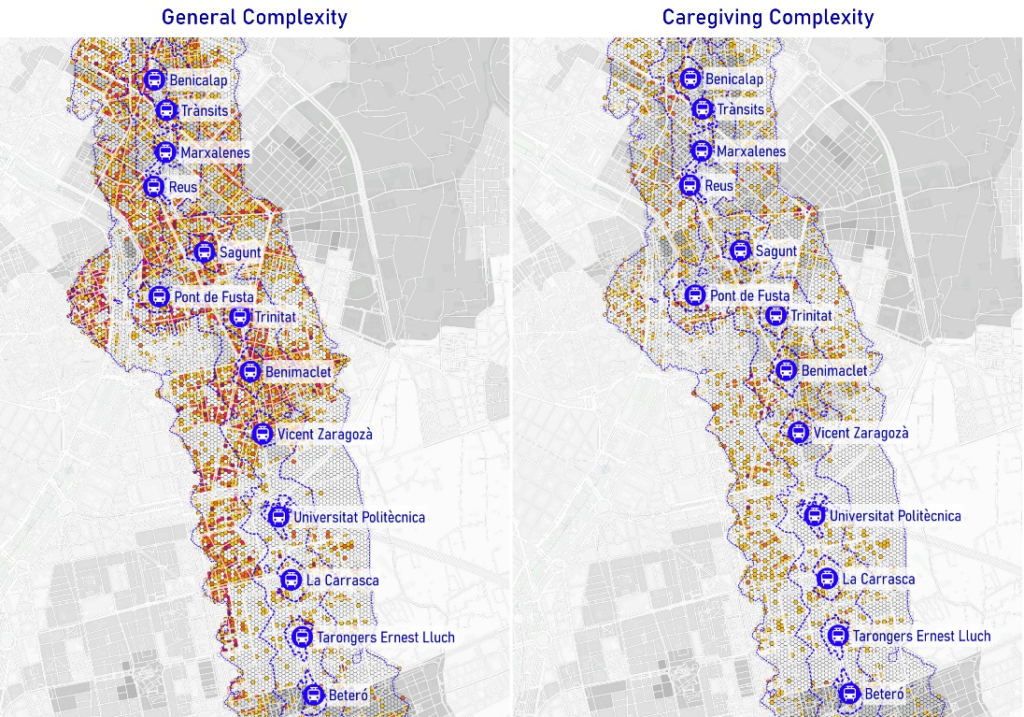
We examine how caregiving-related needs remain overlooked in walkability and Transit-Oriented Development strategies. Despite high levels of urban complexity, many transit-accessible areas lack essential caregiving-support places, particularly in vulnerable neighbourhoods. This spatial mismatch limits care-engaged individuals’ ability to chain trips, and access services, reinforcing mobility and social inequities. Our research highlights the need to integrate caregiving accessibility into planning frameworks to ensure that walkable cities are also inclusive and care-supportive.


