City Know-hows

Target audience
Urban researchers and specialists (urban planners and designers), policy-makers, municipalities, as well as general audiences, particularly those interested in healthy cities and public health.
The problem
The COVID-19 outbreak resulted in severe consequences in the medical field and other areas, including urban planning, education, society, economy, etc. These effects put people’s lives at risk around the globe. Although plenty of studies have been carried out in this area, the lack of a comprehensive guide is the main obstacle to adopting appropriate strategies and policies in cities and urban areas.
What we did and why
The aim of this study was to conduct a systematic review of published research articles on ” COVID-19 and urban studies.” This was done by selecting 63 high-quality articles and analyzing their content based on “publisher,” “origin of research,” “methodology,” “scale,” “subject,” and “solutions.” We believe the thematic classification of the investigated topics and the proposed solutions can be helpful and practical tools for urban researchers and policymakers.
Our study’s contribution
In terms of urban design and urban space:
In terms of physical-spatial and social dimensions along with resilience literature:
Impacts for city policy and practice
Planning and designing urban spaces with a focus on social interactions using creative approaches is the priority in urban planning and design. It also requires exploring scenarios based on place, sustainability, and resilience, as well as government policies for public welfare and the use of collaborative design. Thematic recommendations have also been provided in housing and architecture, smart cities and technology, urban management, environmental sustainability, transportation, and socioeconomic issues.
Further information
UN report: COVID-19 in an Urban World; UNESCO: Cities’ responses to COVID-19; WHO: COVID-19 and social determinants of health, Urban Health; UN-Habitat: Urban Health
Full research article:
COVID-19 and cities: a systematic review of early urban studies by Maryam Roosta, Alireza Gholami & Fatemeh Shahvaran
Related posts

Our collaboration co-created a new methodology reimagining the design, delivery, and management of the Health Impact Assessment using a community lens of the WHOs four interlinking principles: democracy, sustainable development, equity, and ethical use of evidence. We produced an assessment showing the differences between technocratic and experience-led approaches, and shared our methodology with 10 groups from around the UK in a pilot programme who conducted their own exercises locally.
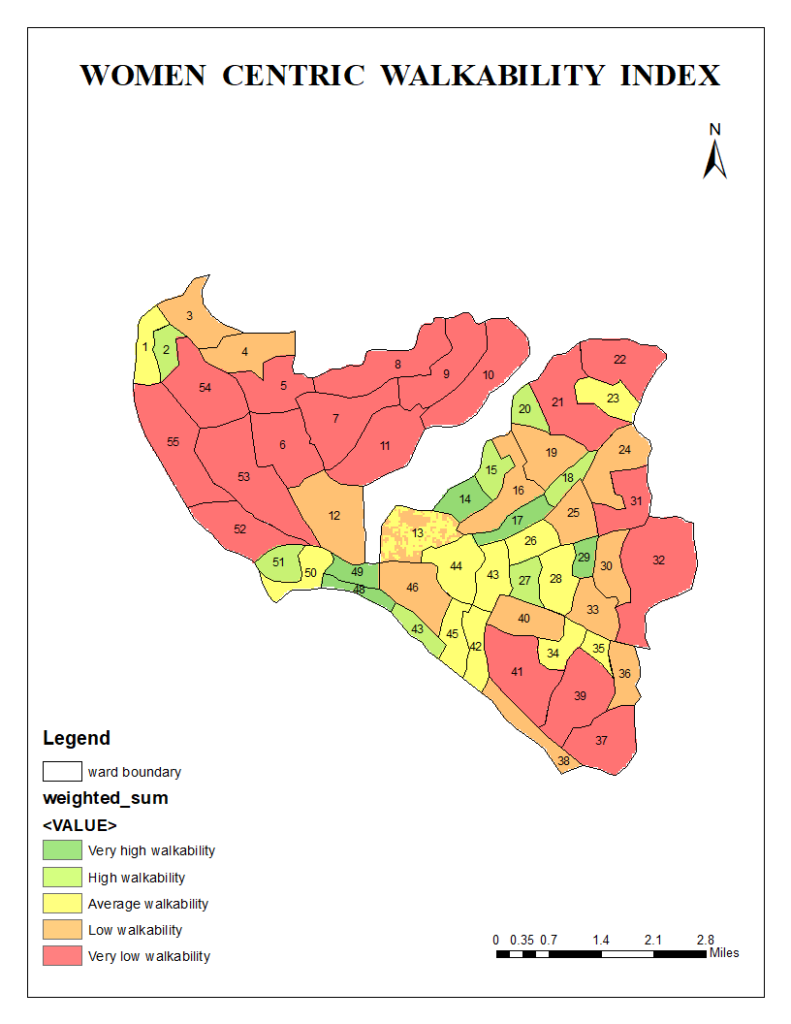
This study introduces the Women-Centric Walkability Index, addressing factors influencing women’s walking experiences in urban areas. Analyzing fifty-five wards in Kollam Corporation, Kerala, we identified key indicators like well-maintained sidewalks, street lighting, safety measures, and access to public amenities that enhance women’s walkability. Using the Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS analysis, our research highlights the need for safer, more accessible, and comfortable walking environments for women, benefiting all pedestrians.

Livability is a people-oriented concept, and accurately measuring it requires a contextual understanding of what local stakeholders deem essential for making communities livable. Despite extensive research on livability indicators, most studies have taken a top-down approach, with few considering the input of the communities.