Contributing factors and indicators of climate resilient and healthy cities
Through a literature review, we summarize key contributing factors of healthy, climate resilient urban environments and how these have been measured. Our study adopts a holistic approach to explore how health and climate change co-benefits could be monitored and achieved in cities. We identify indicators that have been used to measure how policies and built environments support healthy, climate resilient cities. This provides valuable insights for planning, prioritization and monitoring of cities internationally.
Heat, smoke, and urban health: Cooling and cleaner air centres as a tool for climate adaptation in a Canadian urban region
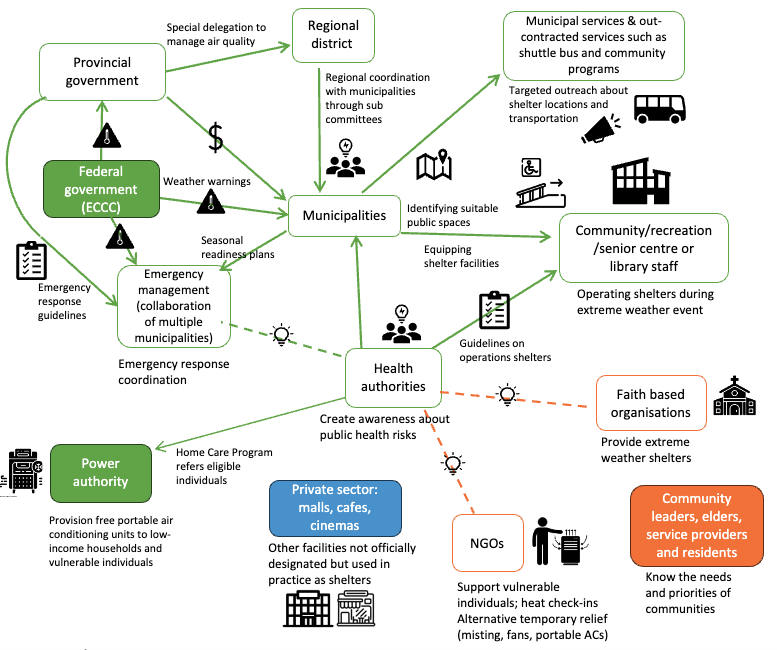
Extreme heat and wildfire smoke are a growing concern in cities. Cooling and cleaner air centres can provide a much-needed respite but too often they’re set up reactively and inconsistently. Our study explores what works, what doesn’t, and how cities can design these spaces to be reliable, inclusive, and accessible for all.
Co-designing healthy and sustainable cities: what Paris residents teach us about urban environmental health

This study introduces a place-based model of urban environmental health drawn from residents’ perspectives.
• Highlights eight interconnected local parameters of environmental health.
• Demonstrates that residents link environmental health to everyday nuisances like noise, air pollution, and lack of safety.
• Shows that viable and livable environments depend on inclusive governance and infrastructure decisions.
• Offers a replicable approach for other cities to assess urban health from the ground up.


