City Know-hows
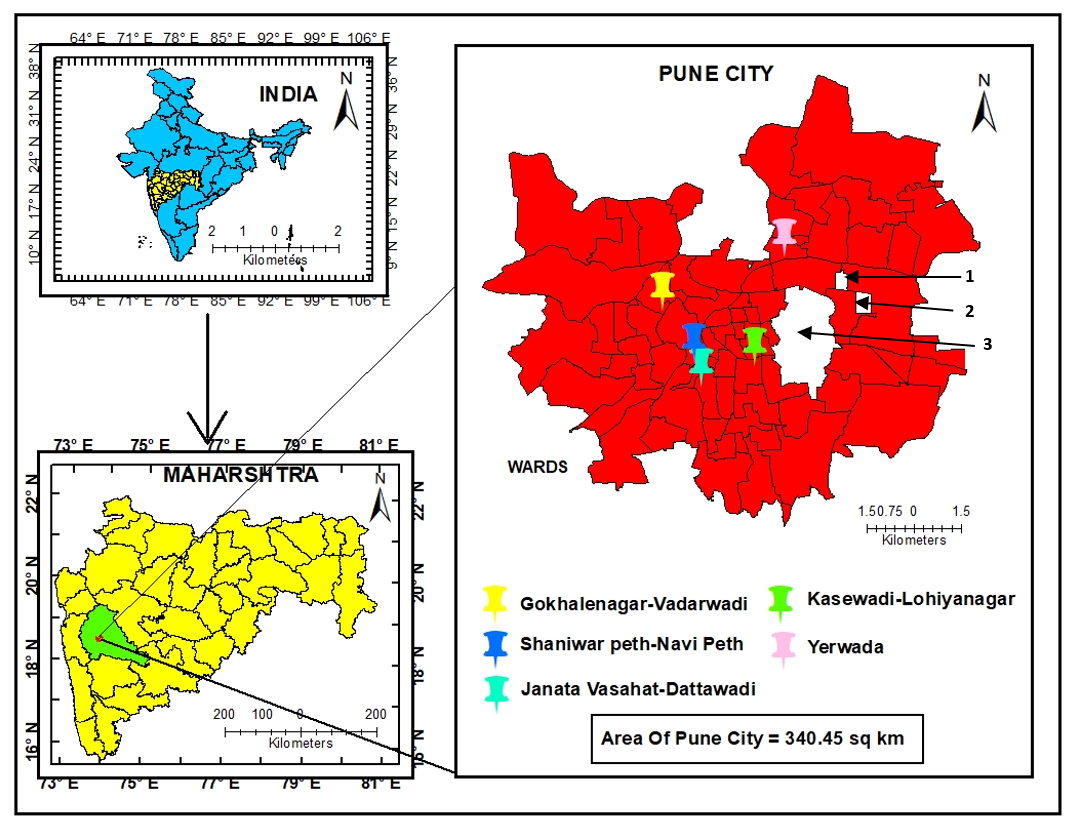
Age-Friendly Communities improve the elderly’s well-being in Pune, through better healthcare, transport, and housing. It is vital to develop age-friendly communities in urban areas.
Share
Target audience
UH-Habitat and relevent community development interests
The problem
We don’t understand how the different dimensions of age-friendly communities impact the life satisfaction of elderly individuals.
What we did and why
Our research involved primary survey data collection and structural equation modelling. The data collected from the survey were analysed using structural equation modelling to determine the relationship between the dimensions of age-friendly communities and the life satisfaction of elderly individuals.
Our study’s contribution
Our study provides insights into the specific needs and requirements of the elderly population in Age-Friendly Communities. This can help policymakers and practitioners to design and implement more effective interventions that promote the overall well-being of the elderly population. In addition, our study provides a comprehensive understanding of the various factors contributing to the well-being of the elderly population, such as social connections, physical activity, access to healthcare services, and environmental factors; all vital components of Age-Friendly Communities.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Our findings can help inform the development of policies and programs that are tailored to the specific needs of the elderly population, such as Age-Friendly Community policy. Thus it can contribute to the creation of more inclusive and supportive communities for the elderly in India and beyond. Overall, this study has important implications for improving the quality of life and well-being of elderly populations globally.
Further information
The WHO Age-friendly Cities Framework: Website.
The Global Network for Age-friendly Cities and Communities: Global report 2018
Full research article:
Contribution of the age-friendly communities in the well-being of the older adults: a study of Pune City by Amey Khare, Anam Fatma, Madhura Bedarkar and Vimal Bhatt
Related posts
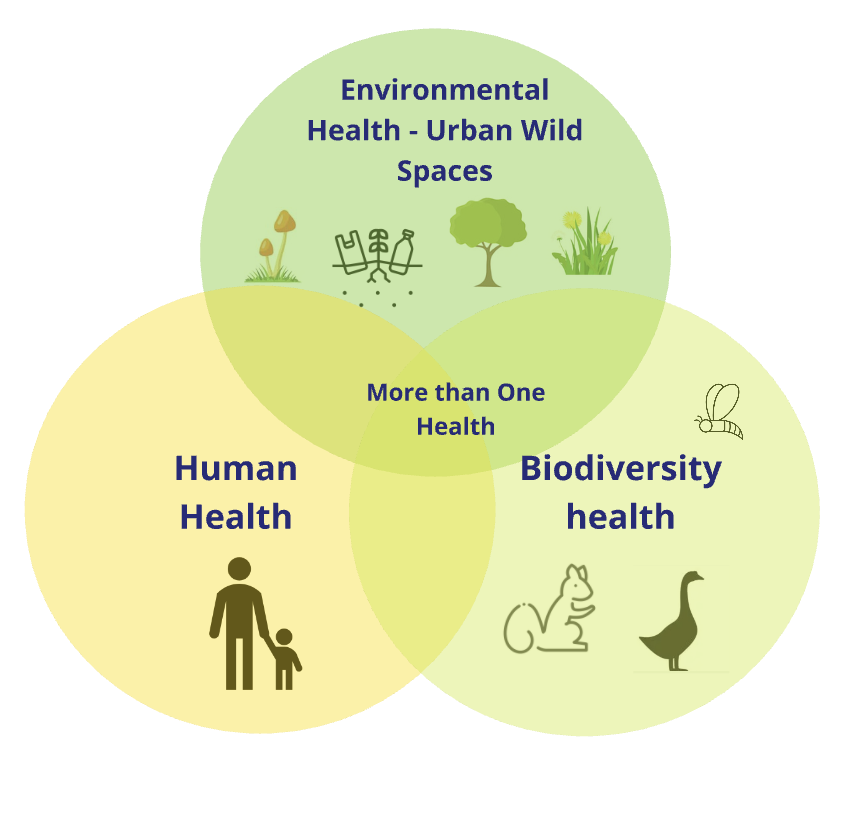
What if urban health went beyond human wellness? Through our more-than-One Health conceptualization, we explored urban wild spaces as places where the health and flourishing of humans, animals, and ecosystems intertwine. This approach provides new insights into designing cities that are not just green, wild, but interconnected as restorative habitats for human and non-human health.

How has the pandemic changed how we use and perceive our home? Many were working, eating, living, playing, sleeping, and learning in the same space. Has changed perceptions influenced ideas of the design of our homes, and potential for happiness and wellbeing?

For perestrain-friendly cities, many studies have tried to show the positive outcomes with different quantitative and qualitative analyses worldwide. However, there are almost no studies that focus on citizens’ points of view and how they experience these positive outcomes. Our study aims to fill this gap. We show that designing walkable cities can change people’s perception of space and have positive effects.