City Know-hows

Target audience
Municipal commissioners of cities and mayors; Actors and decision makers with responsibility for urban housing.
The problem
There is a concentration of tuberculosis patients in the resettlement colonies in M-East ward, Mumbai, which have poor ventilation and sunlight characteristic
What we did and why
We undertook a household survey and calculated sunlight and ventilation parameters in three resettlement colonies using computation models.
We found an association between burden of tuberculosis and poor ventilation and poor sunlight parameters.
We also reviewed guidelines for building resettlement colonies in Mumbai. We did this to demonstrate that poor policies and their execution may lead to preventable public health disasters like tuberculosis which the country is trying to fight.
Our study’s contribution
Our study suggests that design changes need to be made to make the colonies better places for tuberculosis patients to heal and to prevent the further spread of infection to family members and neighbours.
Impacts for city policy and practice
This study supports a demand for changes in policies for the building of resettlement colonies in Mumbai to reduce tuberculosis and support patients healing at home.
It also has international implications where similar living situates are created by bad architecture and poor planning.
In terms of health equity, we ask that policy makers treat the poor and underprivileged same as the rich, in terms of preparing guidelines and policies for construction of housing colonies. Our paper outlines some of the modifications to building design and practice that are required.
Further information
Peehu Pardeshi (@peehu1988), Balaram Jadhav, Ravikant Singh, Namrata Kapoor, Ronita Bardhan, Arnab Jana, Siddarth David, Nobhojit Roy
Full research article:
Related posts

Gentrification is reshaping cities worldwide. It has both upsides and downsides for older adults, including rising costs, housing scarcity, weakened social ties, and mental health issues.

Cities need to be aware of their vulnerabilities to local emergencies. They also need to understand which urban planning, design and management strategies work best to build resilience. We reviewed the latest scientific evidence to identify the most effective preparedness strategies for different emergency scenarios, analysing co- and dis-benefits among them. Ideas and tools for local authorities and communities in general to build back better.
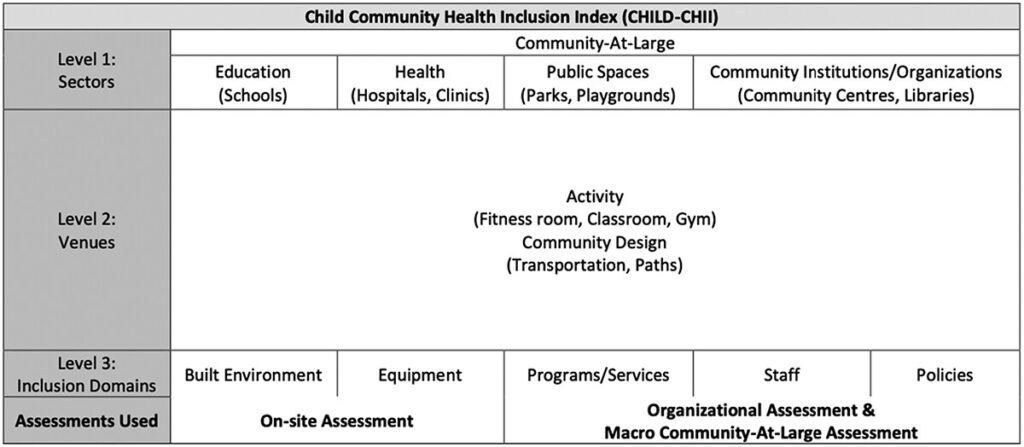
We must take a careful look into the structures, policies, and programs that may be barriers to inclusion of children with disabilities in the community. Assess to intervene and create cities that are inclusive of and healthy for all!