City Know-hows

Target audience
For the attention of: City officials, urban leaders and communities concerned with urban health inequities.
The problem
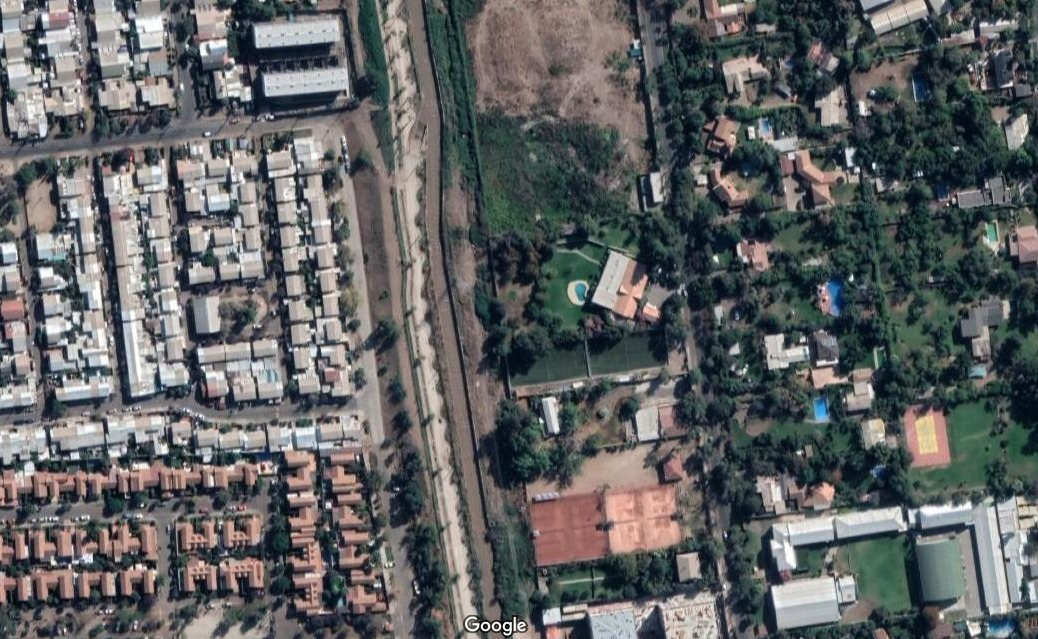
Residential segregation has been proposed as part of the causal path of different health outcomes, however, it has been studied mostly linked to race in a USA context. It has been proposed that there are five theoretical dimensions of residential segregation, and it was confirmed using indices constructed from race proportions. These indices are widely used, however, in Latin America segregation is mostly determined by socioeconomic and educational levels, not by race.
What we did and why
We aimed to evaluate whether the dimensions are maintained when using the educational level instead of race as segregation variable and the Chilean population instead of USA. We worked with census data for the proportion of the population of 25 years or older that have completed university education and replicated the methodology used to determine those five traditional dimensions.
Our study’s contribution
We found that it was not possible to verify the same five dimensions observed in USA from race using the Chilean educational census data. Our study demonstrates the need to locally characterize not only the indices of residential segregation but the theoretical dimensions to which they refer.
Impacts for city policy and practice
There is a need to note that historical and cultural differences between Latin America and USA may translate into different forms of segregation. This means that city/urban policy and practice need to consider that a better characterization of the metrics and dimensions of inequity will improve the interpretations of the effects of segregation on health
Further information
Full research article:
Evaluation of the traditional dimensions of residential segregation by educational level in Chile by Sandra Flores-Alvarado (@sfloresa87), Tamara Doberti Herrera & Mauricio Fuentes-Alburquenque.
Related posts
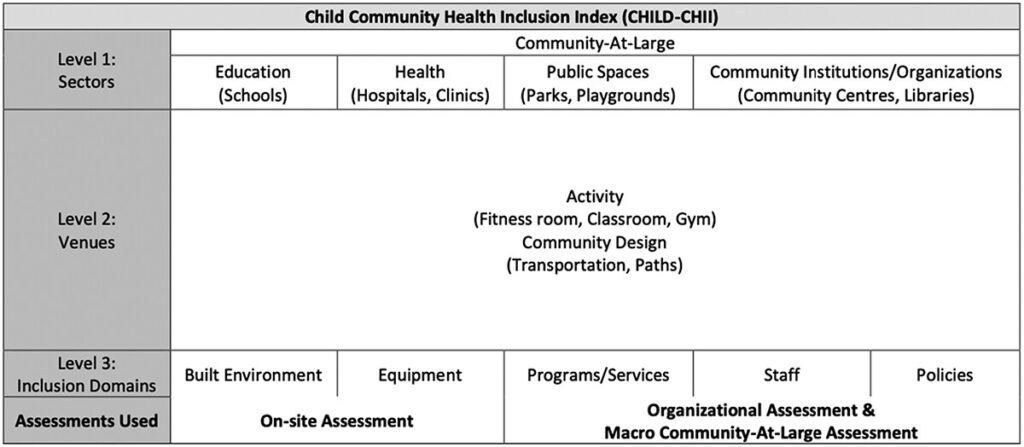
We must take a careful look into the structures, policies, and programs that may be barriers to inclusion of children with disabilities in the community. Assess to intervene and create cities that are inclusive of and healthy for all!
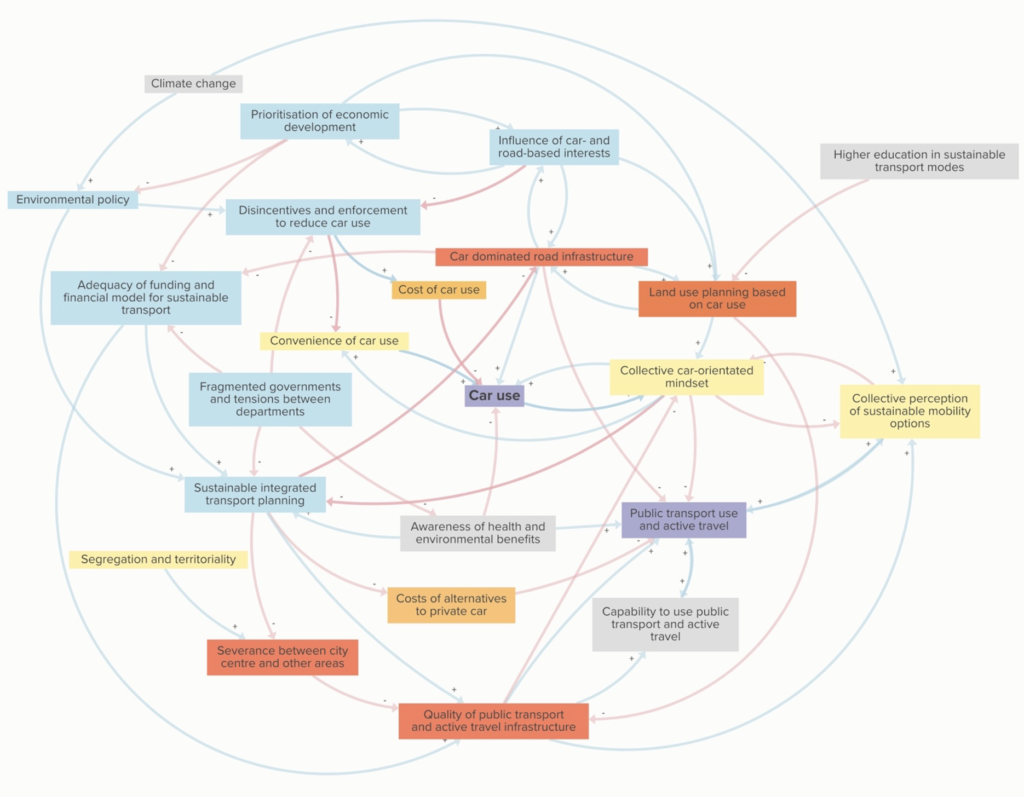
Belfast has very high levels of car use. Working with stakeholders we tried to understand what factors influence this. System wide factors, such as financial models for transport, a collective car-orientated mindset and car dominated road infrastructure, have the strongest influence on individual behaviour.
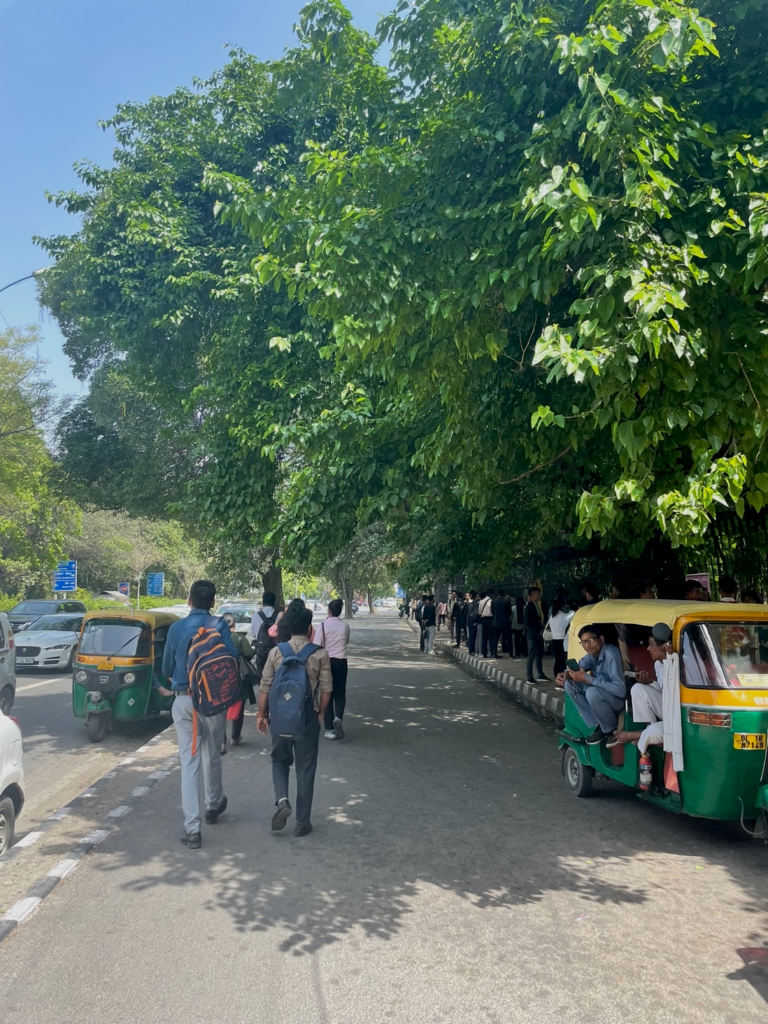

Examining the urban environment is critical for enhancing mental well-being, necessitating the identification of relevant indicators to inform strategic interventions aimed at improving mental health outcomes.