City Know-hows

The by-products of urbanisation, such as air pollution and neighbourhood disadvantage, are often overlooked when studying the impact of urban environments on depression. Understanding how these influence neighbourhood-depression relationships can help inform targeted public health interventions and reduce health disparities.
Share
Target audience
Public health professionals, policymakers, urban planners.
The problem
The creation of age-friendly neighbourhoods is a promising strategy when it comes to reducing depression in mid-age and older adults. Whilst previous studies have explored which neighbourhood features impact mental health, they have failed to consider the moderating effects of both neighbourhood status and air pollution levels. These complex interrelationships must be understood to be able to deliver targeted and effective policy changes.
What we did and why
We wanted to know which features of the neighbourhood environment affected depressive symptoms in mid-age and older adults, and if neighbourhood socioeconomic status and air pollutants in the area impacted these relationships. For this, we used cross-sectional data from the third wave (2011-2012) of the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle Study, a population-based study of Australian adults. We also used the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale to assess depression.
Our study’s contribution
We found that there are significant disparities in depressive symptoms associated with exposure to commercial land use in disadvantaged and advantaged areas with low levels of NO2. People who reside in disadvantaged areas can benefit from commercial locations and facilities if concentrations of NO2 are low, whereas this is not the case for individuals living in advantaged areas. The features required in neighbourhoods to support mental health of its residents also include superior street connectivity.
Impacts for city policy and practice
It is important to address mental health disparities in mid-age and older adults through policy, with disadvantaged neighbourhoods being a priority target for population-level health interventions. In the context of rising levels of air pollutants in Australia and globally, it is critical to consider more stringent air quality standards and low-emission transport options to support mental health. Policy responses should include careful planning and development of land use infrastructure and optimisation of street layout.
Further information
Full research article:
Associations of neighbourhood attributes with depression in mid-age and older adults: the moderating role of traffic-related air pollution and neighbourhood socioeconomic status by Maria Soloveva, Muhammad Akram, Anthony Barnett, Govinda Poudel, Jonathan E. Shaw, Erika Martino, Luke D. Knibbs, and Ester Cerin.
Related posts

Shared mobility hubs that offer (electric) bikes and cars can be a sustainable solution that enables people to expand their mobility options while protecting cities’ environment by reducing private car use and encouraging cycling. We interviewed residents of a deprived neighbourhood in Utrecht, the Netherlands, to understand their mobility needs and views on a recently implemented shared mobility hub in their neighbourhood, identifying potential obstacles in the process.
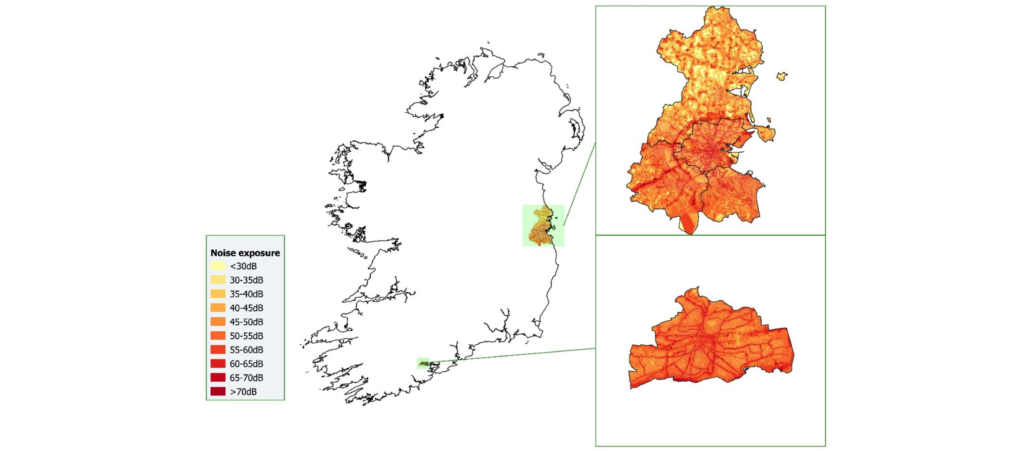
Want to know more about noise and mental wellbeing? Our latest research from two Irish cities.
Citizen science projects can form the basis for sustainable and inclusive urban development in accordance with SDG 11. Citizens, researchers and city authorities work together to explore the city and implement urban planning that meets the needs of all those involved in a city.