City Know-hows

Opportunities exist to influence the growth of secondary cities, home to most of the world’s urban population, in ways that maximise residents’ wellbeing as well as achieve sustainability goals. More research is required to understand how this can be achieved, in particular in relation to city governance.
Share
Target audience
Urban planners and City leaders
The problem
Many aspects of city-living negatively impact residents’ wellbeing and are also linked to environmental degradation. While many of the world’s largest cities are attempting to retrofit solutions to these problems, secondary cities present opportunities to embed sustainability and wellbeing into their growth to avoid repeating problems of the past. In order for this to be achieved, understanding of determinants of wellbeing in secondary city contexts is required.
What we did and why
We conducted a scoping review of the academic literature on determinants of wellbeing in secondary cities. We focused on research in low- and middle-income countries as cities in these contexts experience challenges related to resourcing and governance which may make achieving positive growth trajectories particularly challenging. For the relevant resources we identified, we examined their geographic and thematic spread, considerations of equity dimensions, and conceptualisation of wellbeing.
Our study’s contribution
Our study highlights significant gaps in research which need to be addressed, including:
Impacts for city policy and practice
To aid the growth of secondary cities whilst ensuring sustainability and wellbeing of residents, practitioners and policy makers need to:
Further information
Full research article:
Scoping review of wellbeing research in low- and middle-income countries’ secondary cities
Rachel M. Pateman, Diane Archer, Sitong Mu, Jaee Nikam, Kate Williamson, Rosie Witton & Steve Cinderby
Related posts

Building place attachment and sense of community through design can improve community well-being, yet reviews on this topic are lacking. This manuscript presents a systematic review of the links between pedestrian designs and place attachment and sense of community, and also highlights several health equity considerations to encourage new ideas about inclusive and healthy urban design practice and study.

Public health authorities encourage outdoor activity while physical distancing during the pandemic, but could the built form of cities and neighbourhoods support outdoor activity during COVID-19?
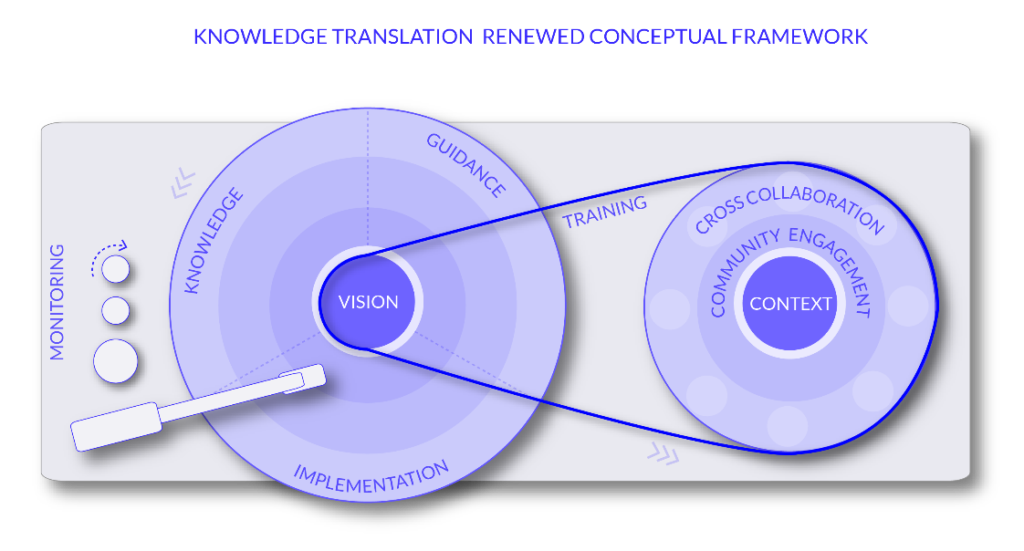
We took a significant step in identifying the existing gaps in knowledge translation for healthy cities and adopting a proactive approach to laying out opportunities for improvement. By developing a visual representation for a renewed conceptual framework, we provide a clear and insightful tool for planners, designers, and policymakers aiming to enhance knowledge translation processes. As a result, this study not only elevates knowledge translation as a field of study for urban professionals but also reinforces its importance in public health.