City Know-hows
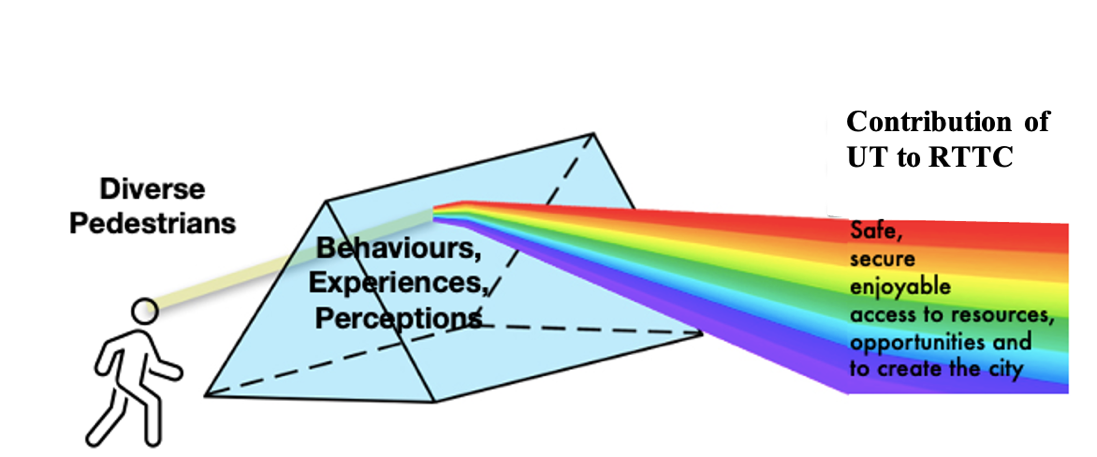
Looking into an urban transformation of a low-income settlement in Maputo, Mozambique, through the behaviours and experiences of pedestrians, shows that physical interventions to the walking environment contribute to the ability of diverse individuals to exercise their Right to the City.
Share
Target audience
Urban leaders involved in transport, public space, settlement upgrading. Communities undergoing physical interventions. Organisations working on low-income, self-built neighbourhoods.
The problem
While spaces dedicated to access such as alleys and roads are ubiquitous and account for a large proportion of cities’ public space, interventions to these areas of the built environment are all too frequently centred on improving conditions for motorised vehicles rather than people. Yes it is walking that is one of the most equitable, healthy and sustainable mode of transport. Therefore, pedestrian experiences are a fit measure of the contribution of urban transformations to residents’ safe and enjoyable access to resources and opportunities.
What we did and why
We examined pedestrians’ accessibility, safety and enjoyment in Chamanculo C, Maputo city in Mozambique, as a reflection of their capacity to use and appropriate their city. Pedestrians were surveyed, differentiating between the residents of two areas where alleys were transformed into streets, in contrast with those in other parts of Chamanculo C. By looking through the prism of a diverse range of pedestrian behaviours and perceptions, we emphasize the public space function of infrastructure for access.
Our study’s contribution
By exploring the characteristics of walking experiences for those residents of two intervention areas compared to two non-intervention areas, we articulate:
• Empirical evidence about walking,
• A methodology to evaluate the impacts of urban interventions through the prism of diverse pedestrian experiences.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Urban interventions, when designed with pedestrians in mind, have the potential to do more than improve mobility; they can reshape the relationship between residents and their city.
Our ‘touchstone’ image uses a prism to metaphorically represent how different pedestrian experiences can shed light on the broader impact of urban transformations. By considering these diverse behaviours and perceptions, urban planners can gain insight into how interventions contribute to the right to the city, ensuring that residents can safely and enjoyably engage with their urban environment and the opportunities it offers.
By enhancing walking accessibility, safety and enjoyment, an intervention can enable individuals to engage with and claim ownership of public spaces. This engagement strengthens residents’ connection to their urban environment. Policymakers and practitioners should consider the broader social impacts of urban transformations, beyond mere physical changes, such as how they influence pedestrians to experience and make better use of their city.
Further information
Full research article:
 From alleys to streets: urban transformation’s contribution to the Right to the City viewed through pedestrian experiences by Maria José Nieto-Combariza, Mercilia Lombe, Sara Marquez, Vanessa Galeano-Duque & Daniel Oviedo
From alleys to streets: urban transformation’s contribution to the Right to the City viewed through pedestrian experiences by Maria José Nieto-Combariza, Mercilia Lombe, Sara Marquez, Vanessa Galeano-Duque & Daniel Oviedo
Related posts

Increasing the availability of urban green spaces, even small pocket green spaces, should be considered a promising intervention for reducing depression among older individuals. Beyond 100m, urban green space protection diminishes. WHO recommends that the population have a green space within a 300m radius. However, for older people, this threshold may be too distant.
However, not all green spaces confer mental health benefits; therefore, researchers and professionals should consider the differential effects of different categories of greenery.

Health arguments are rarely used to justify urban policies in Latin America. A new urban health study suggests we can and should do better connecting
There are so many neighbourhood-level drivers that impact our health that making sense of all the data can be difficult. This tool helps us understand