City Know-hows

Target audience
Those responsible for managing green public space and parks, city government, directors of parks and recreation and green space advocates.
The problem
Current policy prioritizes time to walk to the park as a measure of access. We sought to investigate a more holistic model of park access that would promote equity.
What we did and why
We designed a survey tool based on a comprehensive theory of access. We then performed door to door administration of the survey in two historically disinvested communities bordering a large park in Baltimore City, Maryland USA, to determine factors associated with self-reported park use.
Our study’s contribution
We found that whilst time to walk to the park is an important metric, it is insufficient to describe the barriers to park use in urban communities.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Our finding shows that
Further information
Full research article:
Beyond proximity and towards equity: a multidimensional view of urban greenspace access by Daniel Hindman, Jessie Chien, Craig Pollack.
Related posts

By reviewing the studies on the cities in the early months of the COVID-19 outbreak, we could develop a promising perspective for identifying solutions during future similar pandemics.

This work unveils the heterogeneous preferences of different hospital users for green infrastructure improvements that could improve their health and wellbeing. Moreover, it shows that distinct motivations determine their demand for spending time outdoors and their willingness to pay for these improvements.
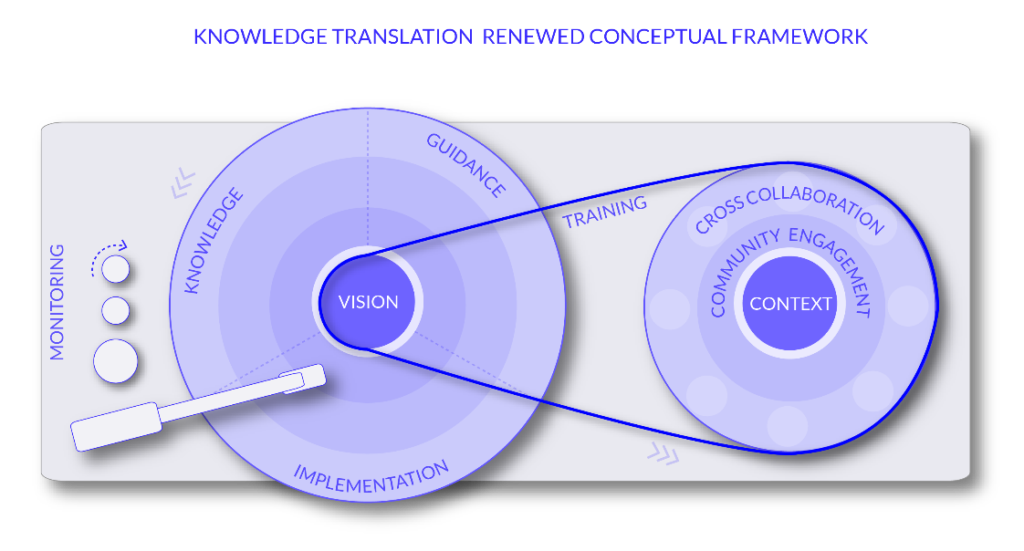
We took a significant step in identifying the existing gaps in knowledge translation for healthy cities and adopting a proactive approach to laying out opportunities for improvement. By developing a visual representation for a renewed conceptual framework, we provide a clear and insightful tool for planners, designers, and policymakers aiming to enhance knowledge translation processes. As a result, this study not only elevates knowledge translation as a field of study for urban professionals but also reinforces its importance in public health.