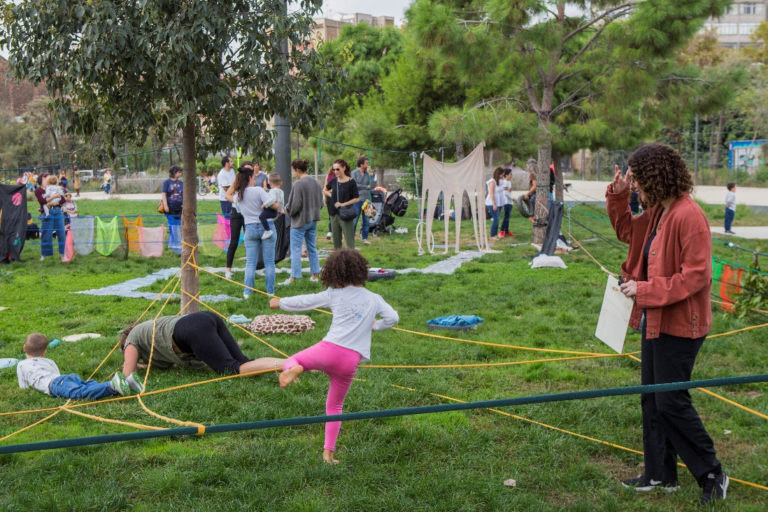
Co-creating public play spaces with autistic children; a co-design method from Barcelona, Spain
Our study explored the preferences, needs, and challenges faced by autistic children when engaging with public playgrounds. Drawing on these insights, we developed a set of evidence-based design guidelines to support neurodiverse-inclusive playgrounds through an autism-friendly, attuned co-creation methodology.