City Know-hows
Health evidence could be used more effectively to influence healthier urban development. We learn from a researcher-practitioner collaboration, involving an embedded researcher in local government working on a regeneration project, which helped to develop a new health modelling tool for environmental change and influence decision-making.
Share
Target audience
Urban development practitioners, academic funders for health and planning
The problem
Health evidence doesn’t effectively influence urban development decision-making. Although there is evidence showing how environmental features can influence health risks, urban development too often results in unhealthy environments.
What we did and why
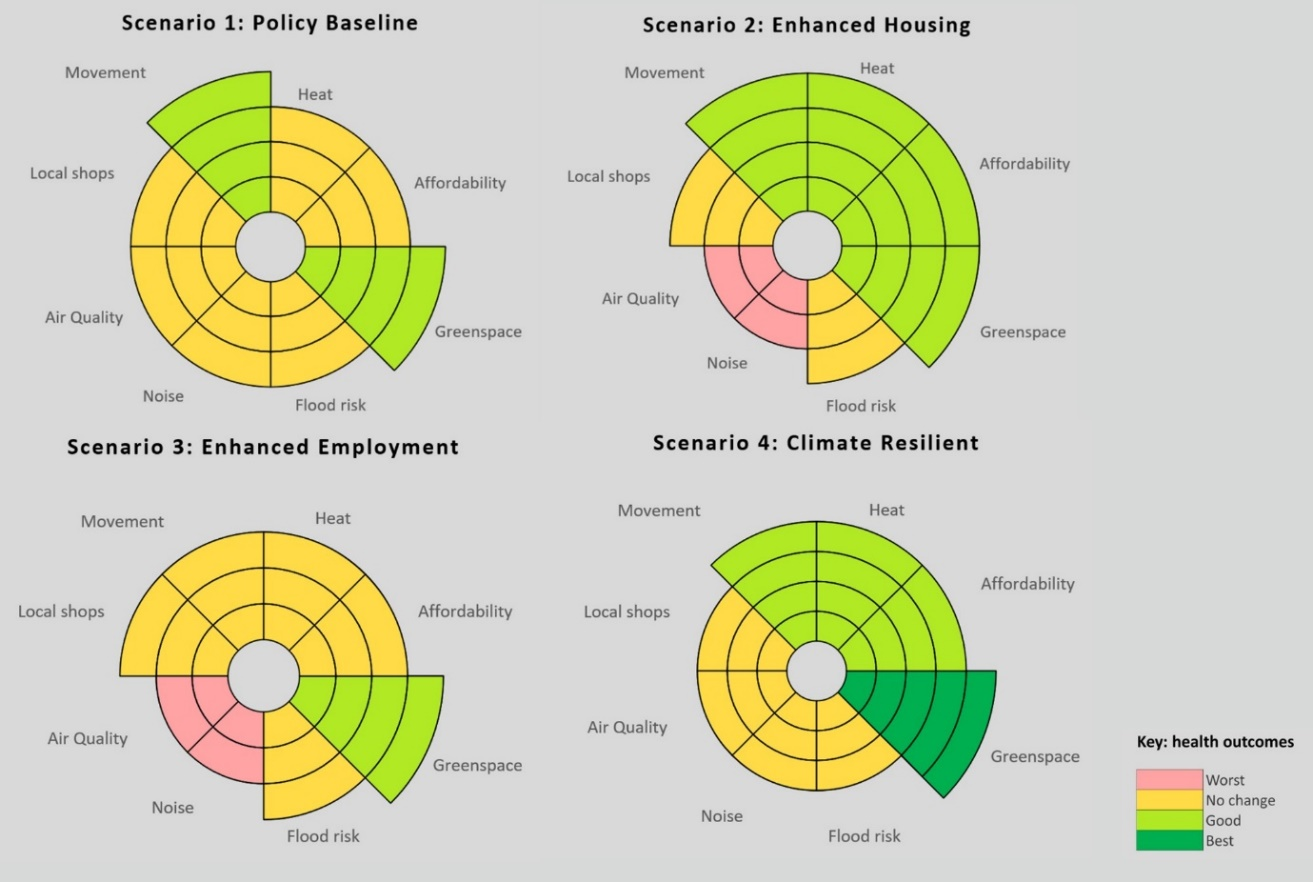
We used an embedded researcher to collaborate with practitioners on a regeneration project who bridged between academics and practitioners to provide contextually relevant health evidence to influence the development of a regeneration spatial framework. This helped develop a new health modelling tool demonstrating impacts of health from environmental change.
Our study’s contribution
We demonstrate the value of showing contextually relevant health evidence to influence urban development decision-making. Health evidence was used to: highlight problems; support good/aspirational solutions; and consider trade-offs in a complex system. This should be recognised to ensure evidence is appropriate for different purposes.
Embedded research is an emerging approach and this study demonstrates its value to support researcher-practitioner collaborations to understand a complex system and develop impactful, timely interventions for healthier place-making.
Summary briefing notes about this study: Using-health-evidence-to-influence-urban-regeneration-in-Bristol-1.pdf
Summary briefing note about the HAUS modelling tool: Valuing-the-external-social-costs-of-unhealthy-urban-developments-1.pdf
TRUUD study. Research about healthy urban development, which this study was part of: https://truud.ac.uk/
Impacts for city policy and practice
A new health modelling tool was piloted in this study. The academic-practitioner partnership helped academics understand a complex system and provided contextually relevant evidence for practitioners to: highlight problems; support good/aspirational solutions; and consider trade-offs.
It shows its value to demonstrate contextually relevant health evidence to influence healthier urban development. More collaborations between public health and urban development sectors could improve the influence of health evidence on urban development decision-making.
Further information
Full research article:
 Using health evidence to influence healthier urban development: A qualitative evaluation of a researcher–practitioner collaboration by Anna Le Gouais, Eleanor Eaton, Katharine Hanss, and Judi Kidger
Using health evidence to influence healthier urban development: A qualitative evaluation of a researcher–practitioner collaboration by Anna Le Gouais, Eleanor Eaton, Katharine Hanss, and Judi Kidger
Related posts

Our study explored the preferences, needs, and challenges faced by autistic children when engaging with public playgrounds. Drawing on these insights, we developed a set of evidence-based design guidelines to support neurodiverse-inclusive playgrounds through an autism-friendly, attuned co-creation methodology.

New research explores if and how mosquito-borne diseases are considered in city resilience, and provides recommendations on how cities can integrate mosquito-borne disease prevention and control into their resilience approach.
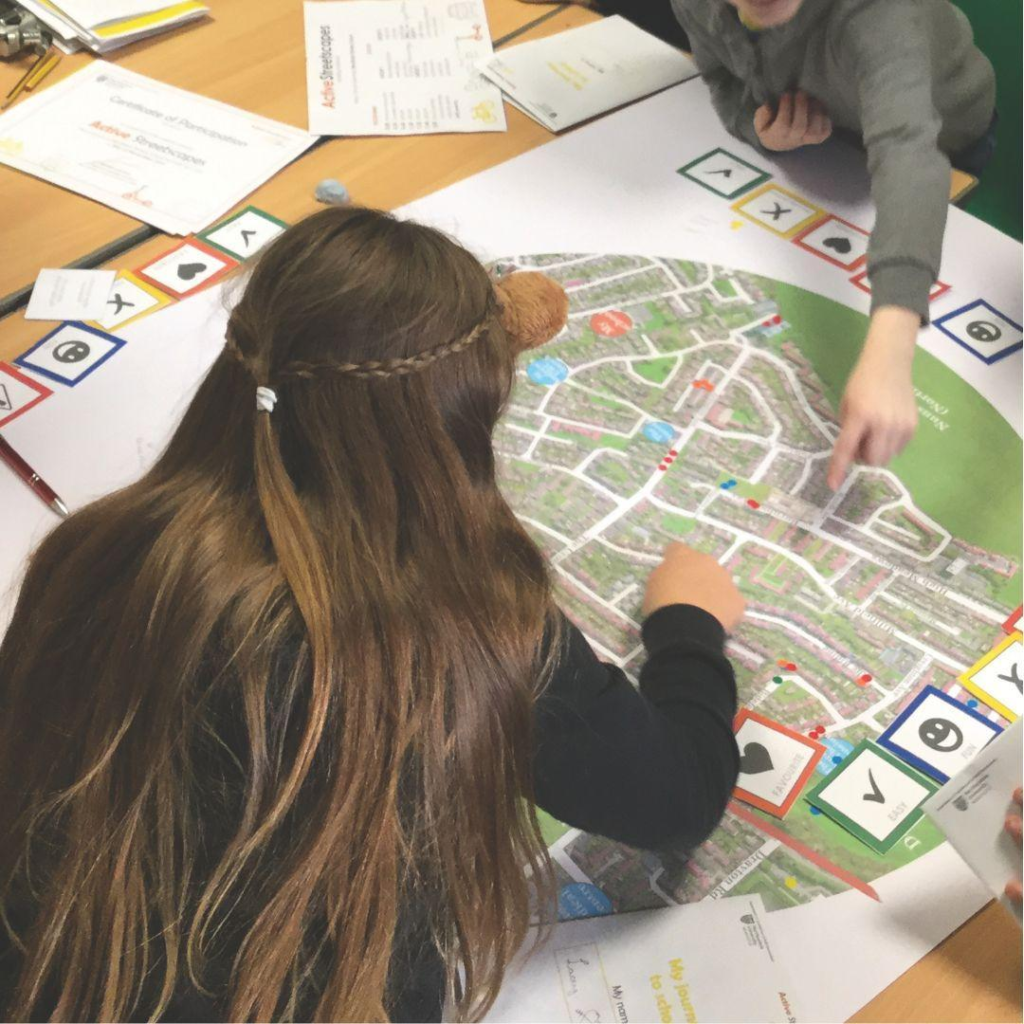

We worked with 82 primary school children (aged 9-10) from four schools and neighbourhoods in Newcastle upon Tyne, UK. Through focus group discussions, we asked them to share their travel experience in their neighbourhoods. Using age-appropriate maps and playful stickers, we gathered insights into their experiences, to identify patterns in what children need from their neighbouhoods. In addition, we mapped their comments to specific locations to better understand the relationships between the built environment features and children’s experiences.