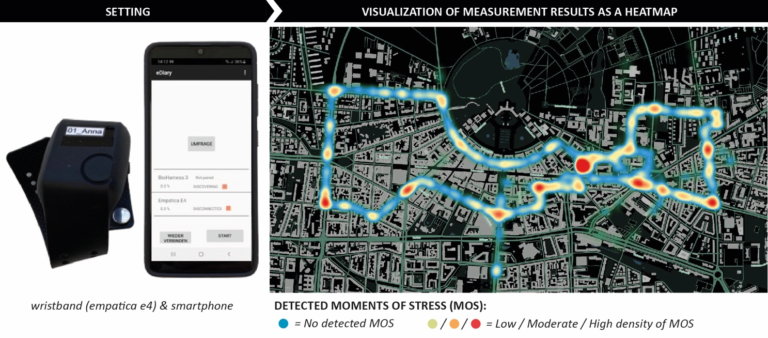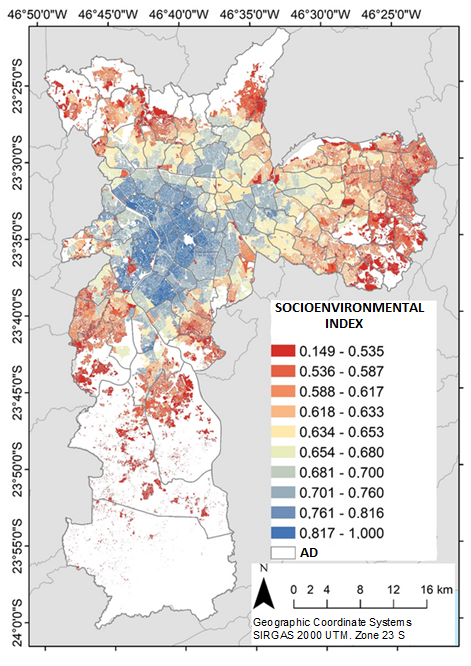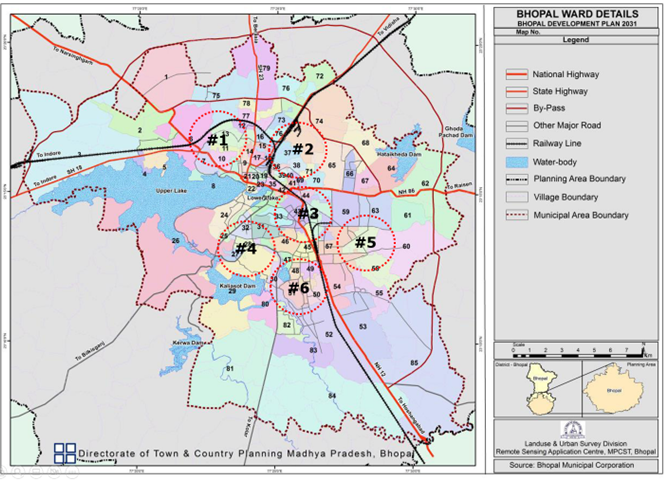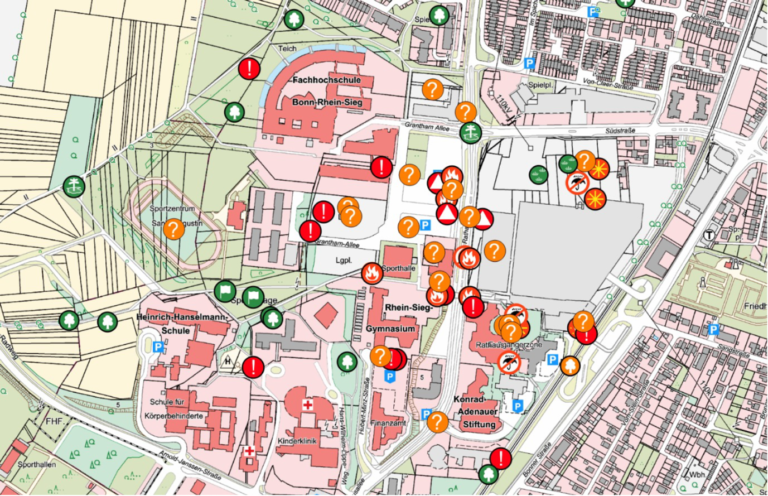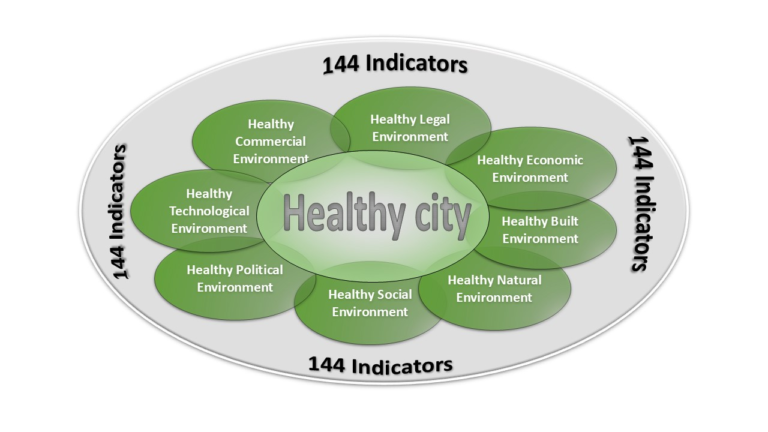
What really matters from the perspective of experts? A set of 114 indicators to measure a city’s health towards building healthy cities in India.
What makes a city truly healthy? This study engaged experts worldwide to identify 144 key indicators across social, economic, environmental, legal, technological, and commercial determinants of health—offering a practical roadmap for India’s mission to build 500 healthy, inclusive, and sustainable cities.