City Know-hows

Target audience
Policymakers for city and town planning and development, urban planners, urban designers, public health practitioners.
The problem
The evidence suggests that there is a link between greenspace and health. However, most studies to date use a generic measure of greenspace quantity or greenness, not distinguishing between different types of greenspace or vegetation. To be able to inform policy and planning, we need to understand ‘what works best’ and for whom.
What we did and why
To add more nuance to our understanding, we investigated the role of different types of greenspace in the mental health and well-being of youth living in London. We distinguished between ‘any green land cover’, ‘parks & gardens’, ‘natural & semi-natural urban greenspaces’, and ‘outdoor sports facilities’, and calculated proportions in 500m around adolescents’ postcodes. We then linked these exposures to mental health and well-being outcomes in 10- to 15-year-old adolescents.
Our study’s contribution
This study adds to an evolving stream in the literature, not only assessing the role of mere quantity of (any) greenspace but distinguishing between different types of greenspace. In this study, findings were inconclusive, however, we identified interesting patterns. For example, parks & gardens and outdoor sports facilities seemed to be more ‘beneficial’ than natural & semi-natural urban greenspaces. Overall, however, no clear conclusions can be drawn, and further studies are needed to shed light on the nuances of associations.
Impacts for city policy and practice
This study is only one contribution to an evolving stream in the literature. More studies are needed to shed light on the nuances of the associations of greenspace with health in general, and with mental health in adolescents in particular. It is important to remember that there are many types of greenspace and many different demographics. Ideally, at some point, we will have a better idea of ‘what works for whom’ to make more informed policy and planning decisions
Further information
Full research article:
Types of greenspace and adolescent mental health and well-being in metropolitan London by Marie Mueller, Emily Midouhas and Eirini Flouri.
Related posts

Make the neighbourhoods of your city age friendlier by using tools that support more informed decision-making. Are you an urban planner or a policy maker interested in knowing how age-friendly the neighbourhoods of your city are? Would you like to know how to improve them?
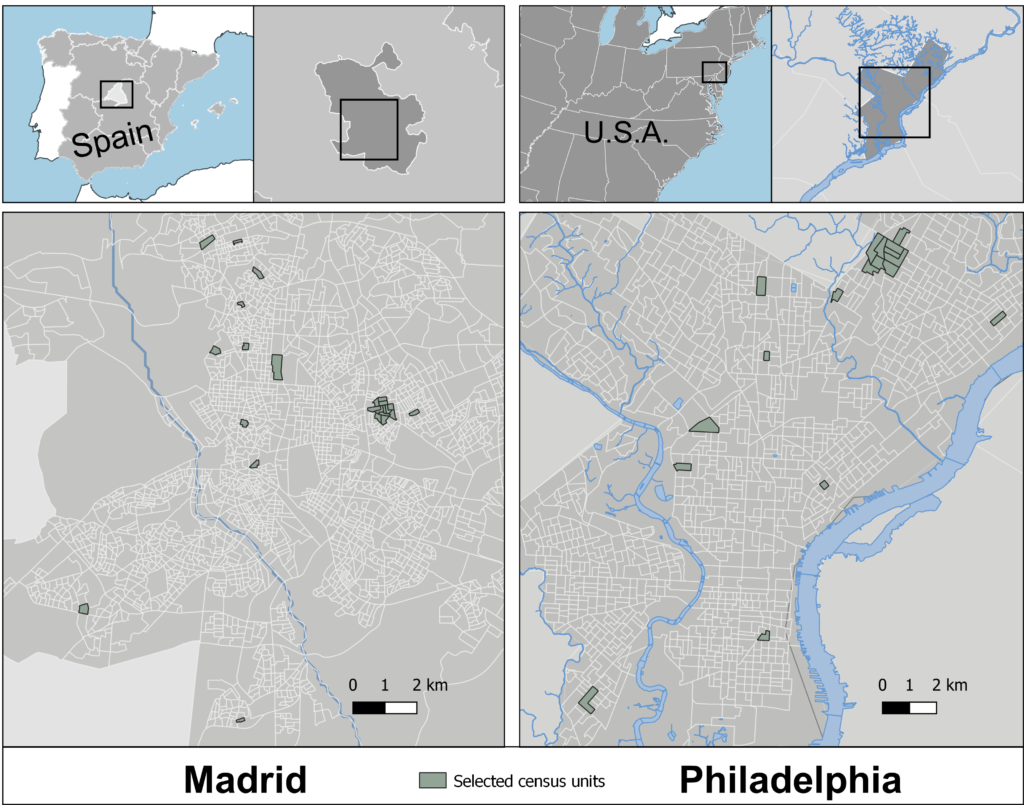
We compared cross-city differences in the walking environment in Madrid and Philadelphia as a case study
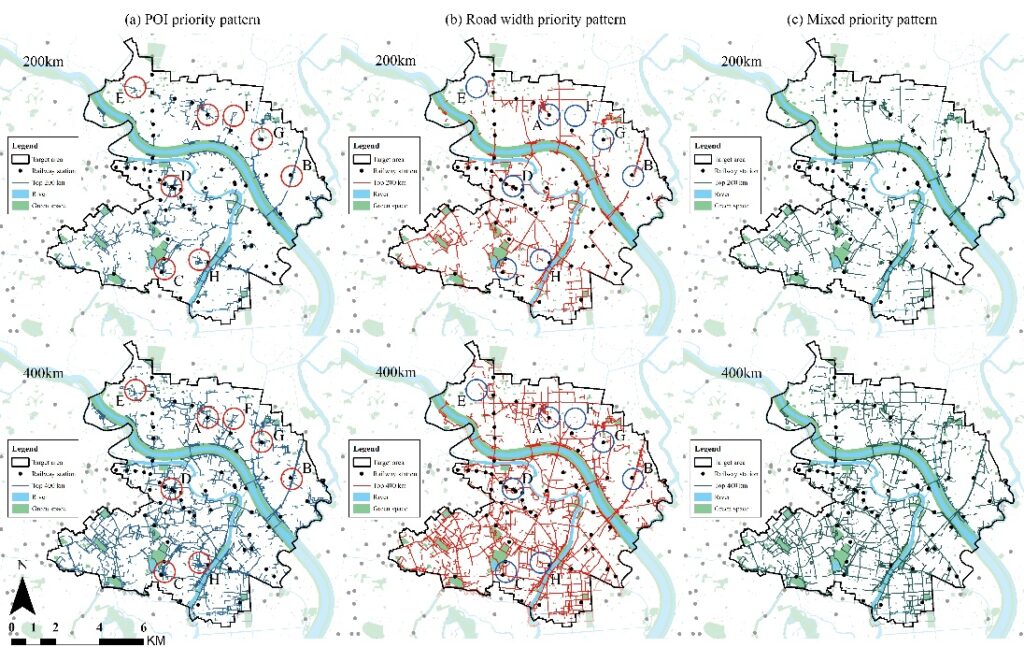
A case study in Tokyo reveals how road width, green spaces, and local amenities influence joggers’ route selection, drawn from extensive data analysis. These insights hold significant implications for urban planning strategies, advocating for city designs that prioritize exercise and outdoor activities.