City Know-hows

Target audience
Take note: City officers, policy makers, landscape architects. Indigenous communities and people working with indigenous communities worldwide.
The problem
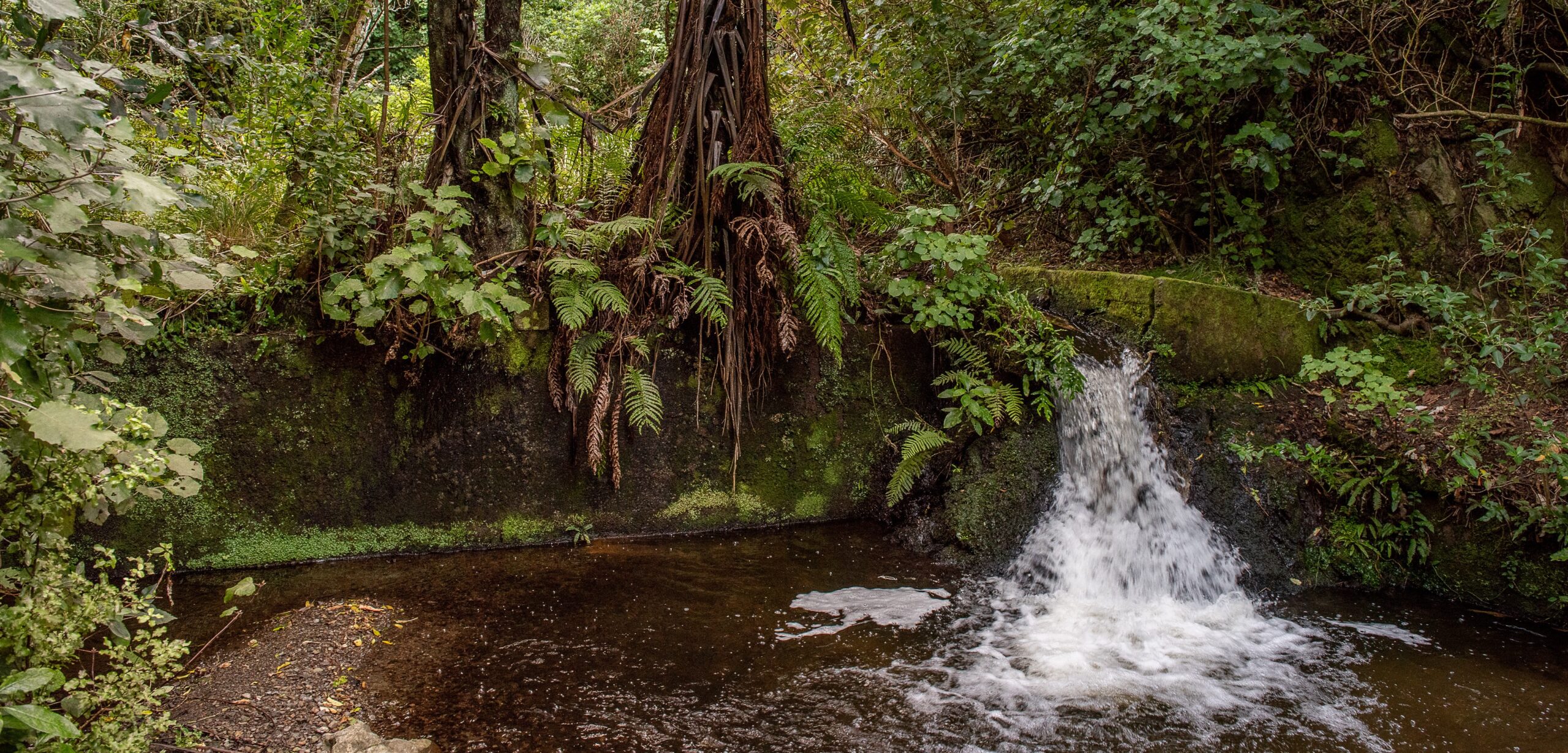
In the current context, in New Zealand, traditional, cultural and ancestral landscapes have been desecrated by growing demands from colonization, capitalism, urbanization and globalization.
What we did and why
We explored the potential for reinstating the ideologies associated with traditional indigenous knowledge and, in particular, the intricacies of interconnectedness between environments and people. We examined new ways of integrating Māori knowledge in landscape architecture and landscape design to renew and expand the concepts of belonging, identity, quality of life and place.
Our study’s contribution
This study adds to the understanding of where identity and wellbeing fit when we design for architecture or landscape architecture. It also adds to our;
The study show the importance of the consideration of traditional indigenous knowledge as a catalyst for truly understanding site context and design outcome.
Impacts for city policy and practice
Based on this study we suggest:
Further information
Full research article:
Haumanu ipukarea, ki uta ki tai: re-connecting to landscape and reviving the sense of belonging by Bruno Marques, Jacqueline McIntosh and William Hatton.
Related posts
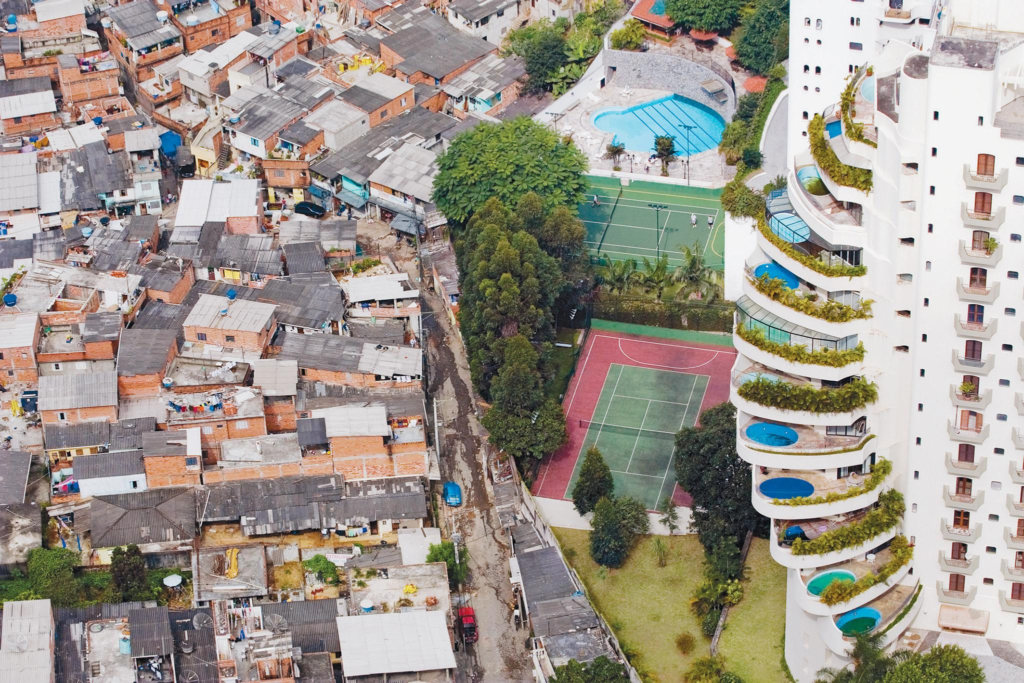

A Brazilian study, in Sao Paulo, Brazil, showed important changes in built environments for physical activity, highlighting these chances across different regions of the city,
From data to policies: let the data speak! Making local policies more evidence- informed about health and health inequalities. Developing a community engagement toolkit to address health inequalities in urban settings.

The involvement of citizens in nature placemaking processes can have a positive impact in the psychological health and wellbeing. The connection with the natural environment and community is grounded in five core principles recognized as the 5Gs: Gracious, Green, Giving, Grounded and Grateful, as conveyed through the activities.