Community voices on outdoor gyms: A qualitative study among municipal officials and residents from Arab localities in Israel
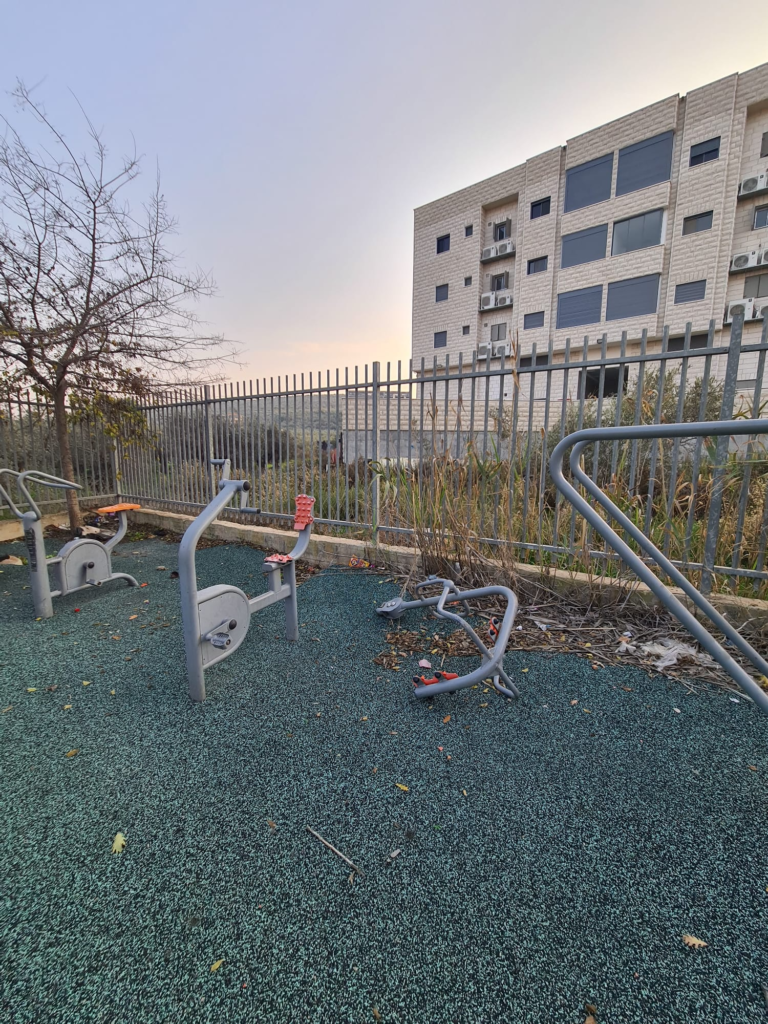
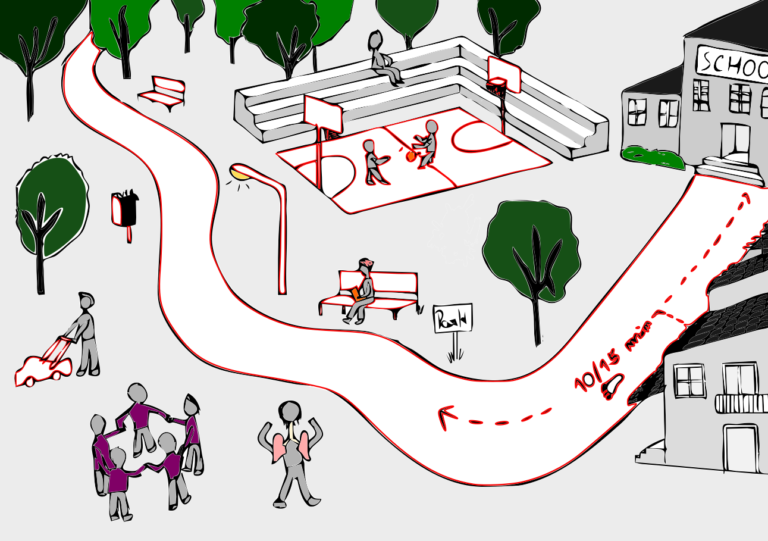
We interviewed ten municipal officials and 23 residents in four Arab towns, and observed five outdoor gyms. We wanted to understand how outdoor gyms are perceived, what barriers limit their use, and what strategies could make them more effective. This was the first study of its kind in Arab towns in Israel, but it also speaks to underserved communities worldwide where informal urban development and limited resources shape access to healthy environments.